How IoT is Revolutionizing the Insurance Sector: Use Cases and Benefits
|
Listen on the go!
|
Traditional businesses are projected to be disrupted and revolutionized at an unprecedented rate as the Internet of Things (IoT) emerges. These new technologies have the potential to benefit the insurance business, which has been hesitant to adapt in the past.
Before understanding how the Internet of Things will affect insurance, let’s define what we mean by “IoT” in this context. In a nutshell, IoT refers to the internet-connected connection of physical items or devices known as “Things” with sensors, software, apps, servers, and other devices. It allows data to flow between devices and sensors, and it allows devices to interact, collaborate, and learn from one another’s experiences in the same way that humans do.
More than 26 billion of these networked devices are already in use, with the number expected to rise to 75 billion by 2025. The IoT’s ability to dramatically boost efficiency and add capabilities across a wide range of businesses is due to the widespread availability of devices with connective capabilities and the possibility of real-time communication between them.
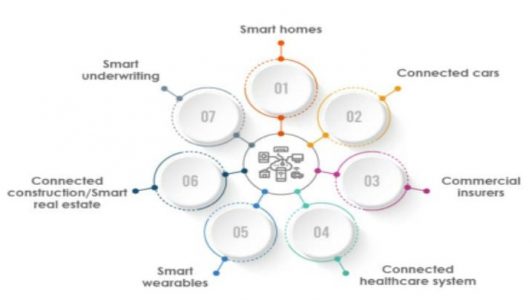
Some Important Use Cases of IoT in Insurance
In the IoT-driven insurance industry, connected devices collect data on homes, cars, and health, leading to more accurate risk assessments and tailored coverage plans.
Here are some of the important use cases of the IoT Insurance Industry.
Smart Homes
Smart houses are one of the most promising fields. Smart doorbells, smoke alarms, and security systems are increasingly commonplace in many homes. Insurance firms could provide services to avert accidents and provide better service to customers if they had access to this device’s data. Here are a few examples:
- Moisture sensors or thermal cameras could detect mold in a wall and warn of the possibility of a water pipe leakage before the damage becomes too extensive, turning a minor maintenance task into a large claim to repair the damage, host customers during the maintenance period, and pay for damaged goods.
- People pay a lot of money each month for vigilance services. Smart bells, window/door sensors, and human detection cameras might readily identify a robbery and alert the authorities, lock doors, turn off lights, and record the various divisions of the house.
- While no one is home, smart smoke and fire alarms could detect a fire sparked by a short circuit and instantly summon firemen. This would save a lot of money in terms of the expensive claims for damages and lost items that are common in this situation.
Connected Cars
Telematics is now being used to connect cars to IoT apps. Insurance firms can track driver behavior via telematics, which allows them to monitor the driver’s routes, speed, acceleration, and steering wheel rotation in real-time using a basic mobile device (or even a mobile phone app). We can track engine temperature and pressure, oil level, brakes, seat belt detection, human presence detection, temperature and humidity within the car, and dozens of other metrics by having real-time access to these variables. This information can then be applied to:
- Measure how safe each individual journey was using machine learning algorithms by analyzing the sensor data and using those rates in the dynamic policies to reward good behavior and add penalties in the case of an infraction or risky behavior.
- Predictive Maintenance using anomaly detection machine learning models to quickly detect a need for maintenance in the brakes, engine, oil, etc., before something crashes and turns into a much higher claim for repairing the damages.
- Reduce fraudulent claims by analyzing the collected data in the event time frame to understand if the driver was negligent. It was caused on purpose if the impact measured by the sensors and the driver’s behavior matched the report description.
- Warn in case it detects the presence of a human being or animal forgotten inside the car and activates an emergency plan with a warning to the customer, opening windows, turning on air conditioning, etc.
- A camera to detect the driver’s facial expression and detect dizziness, drowsiness, or alcohol , throw a warning, or automatically stop the journey safely.
- Gamification of driving promoting defensive behavior, gas-saving, and a measure of how ‘green’ their driving is.
This is only a tiny sample of the services we may provide to our customers to improve their safety (and hence minimize risk) while simultaneously providing excellent service and preventing churn to our competitors.
Commercial Insurers
Commercial insurers use IoT devices, apps, and sensors integrated into industrial units to create a dynamic rating model that allows them to offer risk-based pricing to their customers. IoT apps that provide real-time data help insurers control risk and reduce losses dramatically.
Connected healthcare systems
Smart Health gadgets can potentially cut health and life insurance risk dramatically. There are bracelets that cost less than $30 that can assess our heart rate and sleep quality in real-time, as well as devices that can measure our blood sugar, among other things. The following instances might be readily achieved if our customers used these:
- Elderly people seek smart devices that provide them with independence. Using these wearables could automatically activate an emergency plan in case of passing out or falling.
- Bracelet and scale, as well as other health equipment, to monitor heart rate, weight, fat, tension, and so on, promoting good habits and exercise in exchange for price discounts, prizes for goals met, loyalty plans, and so on.
- Socks or shoes that can alert diabetics to potential ulcers and others that can prevent future high hospital claims, medical surgeries, disability claims, etc.
Again, there are various alternative products and services that would benefit the insurance firm and the customer.
Smart wearables
Fitbit, Fitband, other smart health wearables, and smart health apps like Google Fit, Strava, Sports Tracker, and others make tracking and monitoring an individual’s health simple and inventive. Insurers use this real-time data to personalize policies and provide savings to people who live a healthy lifestyle.
There is a wealth of health-related data available for life insurance.
That includes:
- Steps Per Day
- Heart Rate
- Blood Pressure
Life insurers can utilize this to obtain a quick and accurate picture of a customer’s health. When it comes to calculating risk, this is useful. The number of steps taken daily is a highly accurate predictor of mortality.
The watches are significantly subsidized, and if the users are particularly engaged, they can be further subsidized (all the way to $0). What’s the result? A 68 percent drop in life insurance claims and a 20% increase in physical activity among policyholders.
Connected construction/Smart real estate/Industry
The real estate industry is fiercely competitive and fraught with danger. IoT connects job sites, machinery, and people, allowing insurers to digitally monitor the site, analyze land stability, and collect real-time data.
Because the market comprises so many different insurance products, each area has its own set of options. The following are some more generic examples that apply to all industries:
- Embedded sensors in commercial infrastructure to monitor environmental conditions, detect smoke, CO2, mold, and other measures, and automatically adjust the environmental conditions to prevent potential harmful events.
- Wearables on workers to track location and warn if they get close to a dangerous place. Also, this would prevent fraudulent claims of workplace accidents.
Smart underwriting
In the past, insurance brokers had to collect and rely on data provided by applicants. The underwriting process has grown more efficient and speedier since the introduction of IoT apps in the insurance industry. Insurers can establish a better and more precise client portfolio, analyze risks in advance, reduce losses, and improve policyholder interactions.
Advantages of IoT product Insurance
Now let’s head into the critical part: how exactly can companies benefit from adopting IoT Insurance solutions?
New revenue sources
Customers pay payments in exchange for insurance coverage, which is how insurance firms make money. New services and products with high market demand, such as predictive maintenance, monitoring, and control (vehicle, asset, person, and pet), energy consumption, security & surveillance, building management, telemedicine & healthcare, everyday things, and service recommendations, can be developed.
Insurance companies might use IoT to cross-sell to their clients. With more information about customers and their habits, there may be opportunities to recommend new customized products, make personalized recommendations, and build a network of partners, such as car repair shops or MoT specialists, where repeat business and commission opportunities can be explored.
Reduce costs
Insurance firms can save a lot of money by using IoT data to construct better fraud detection models with sensor driver decisions, which will help them save billions of dollars each year by simply detecting fraudulent claims by analyzing sensor data.
Because underwriters will have far more data from each consumer to create a personalized risk analysis, a more accurate risk assessment will be available. Dynamic insurance policies will not only protect insurers by imposing penalties for bad behavior, but they will also encourage customers to be more cautious by rewarding good behavior.
Predictive Maintenance and Warning Services will save billions of dollars each year since removing a probable cause of an accident (for example, a leaking pipe) is significantly less expensive than replacing all of the damage caused by the accident, which would result in a much larger claim.
Improve the customer experience and relationship
Unless there is a claim, there are only two points of communication between the insurer and the customer: the first when the conditions are agreed upon and the second during the renewal or cancellation procedure. Insurers rarely communicate with the individuals they serve; when they do, it’s usually through automated emails or phone calls. Insurance firms find it challenging to create strong relationships and engage clients since they have limited exposure to them over time.
We can engage with clients more frequently now that we have real-time information about them by offering new services such as warnings, recommendations, loyalty programs, and reward systems for good conduct. This provides a whole new level of client experience, presumably lowering churn rates and allowing us to be more competitive, not just by lowering premium costs.
Optimization of Risk Assessment and Prevention
Insurers can take a proactive rather than reactive approach by utilizing IoT data. Teams can now foresee the occurrence of events rather than reacting to issues or occurrences after they have occurred. For example, in the case of a boiler failure in a business building, the insurer could notify the policyholder before any significant damage occurs. As a result, customers feel safe, increasing brand loyalty, retention, and trust.
Insurance firms can now raise their value proposition from risk coverage to risk prevention, which gives clients a better value and overall experience, thanks to the revolutionary new capabilities afforded by IoT. Encouraging consumers to install equipment such as working fire alarms, water leakage alarms, and heat and gas sensors in their homes, commercial buildings, or enterprises, for example, can assist in preventing property damage and high costs. These sensors, like security devices, can notify the insurance provider and the consumer of any anomalies. Although risk management is not the responsibility of insurance firms, using IoT for this purpose can generate synergy between customers and insurers.
Let’s look at how IoT apps are used in healthcare, automobiles, and home insurance:
Health Insurance
Insurers now have greater client data thanks to IoT apps, which they may use to deliver better insurance products.
Health insurance companies can use an insured person’s health information to offer various discounts, including specific rates for nonsmokers, women, and family or partner plans.
Car Insurance
Various data elements, such as credit score, automobile location, car type, kilometers driven per year, age, gender, and so on, are readily available to insurers thanks to IoT apps.
Insurers use this information to provide responsible drivers and customers with improved pricing models, offers, and discounts.
Insurers may use real-time IoT data to notify and assist drivers, minimizing the likelihood of unwarranted claims. In terrible circumstances, such as tragic accidents, IoT sensors automatically notify insurers, speeding up claim processing..
Home Insurance
Home insurers can use IoT apps to collect real-time data and notify homeowners and residents about mishaps such as gas leaks, water leaks, fires, smoke, robberies, etc. And customers benefit, too.
Their advantages include
- Increased insurability. For example, in the past, obese customers would have had limited life insurance options. On the other hand, wearable gadgets can provide more data to illustrate good habits or recent attempts to enhance their health, allowing consumers to access more comprehensive strategies.
- A closer relationship with insurers. Closer data sharing and solutions like communications applications can help insurers and their consumers connect and communicate more frequently.
- The incentive is to make healthier and safer life choices with the possibility of receiving discounts on products that will assist them in doingso.
- A faster path to insurance. Customers who are healthy and responsible can easily submit their IoT data to life insurance and be quickly assigned to a plan.
How can insurers make this happen?
It may be simpler than you think to transition to an IoT-based strategy. Here are some easy steps to follow:
- Develop a plan and choose a direction. Determine which areas you want to concentrate on and whether your customers want to use more IoT devices.
- Build the right partnerships early on. These could be with the manufacturers of wearable devices, for example.
- Consider data privacy laws and other regulations. Customer information is a risky and delicate subject. Ensure you’re taking the proper safeguards and have clear procedures in place from the beginning.
- Prioritize security. Data breaches are all too common; losing customer information to an attack can ruin your reputation and result in serious legal consequences.
Don’t stop at collection. Gathering data is one thing, but to reap the full benefits, you must also consider how to store it, integrate it into your systems, and relate it to your broader plan.
Conclusion
IoT apps link the globe in ways it has never been connected. IoT apps have increased dramatically in the healthcare, insurance, and automobile industries. IoT apps’ ability to detect, analyze, and assess real-time data via IoT sensors and devices is assisting the insurance industry tremendously in providing better insurance services.
Overall, more specialized consumer data, such as sensory data from IoT devices, can assist organizations, particularly insurance firms, in better understanding their clients and potentially providing better services.
Cigniti’s experience with IoT app Testing as a Service (TaaS), a team of IoT-skilled testers, and a robust IoT testing infrastructure (labs, simulators, test racks, and so on) enable real-time testing of Big Data, Compatibility, IoT Security, Performance, Pilot, Regulatory, Reliability, Upgrade, Usability, and smart devices in a dynamic environment (RFID, Sensors).
Need help? Consult our team of IoT Testing experts and Insurance Domain experts to learn more about how IoT is revolutionizing the insurance sector, along with various use cases and benefits.





Leave a Reply